Lead
A metal that has been used for over 2,000 years.
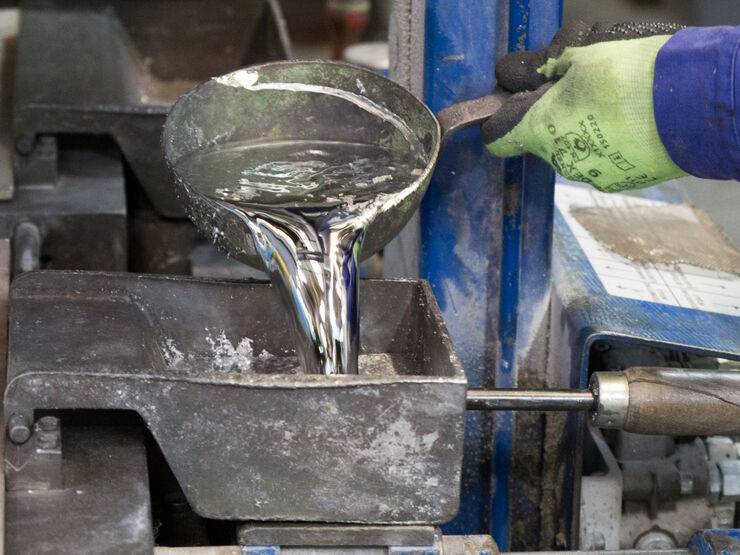

Used for over 2,000 years, lead is a bluish-silver metal historically used for water pipes, decoration, utensil manufacturing, paints, cosmetics, and numerous technical applications. It is infinitely recyclable, with a yield close to 100 %. Today, 60 % of global consumption comes from recycling, mainly from used batteries (85 %).
Production and consumption
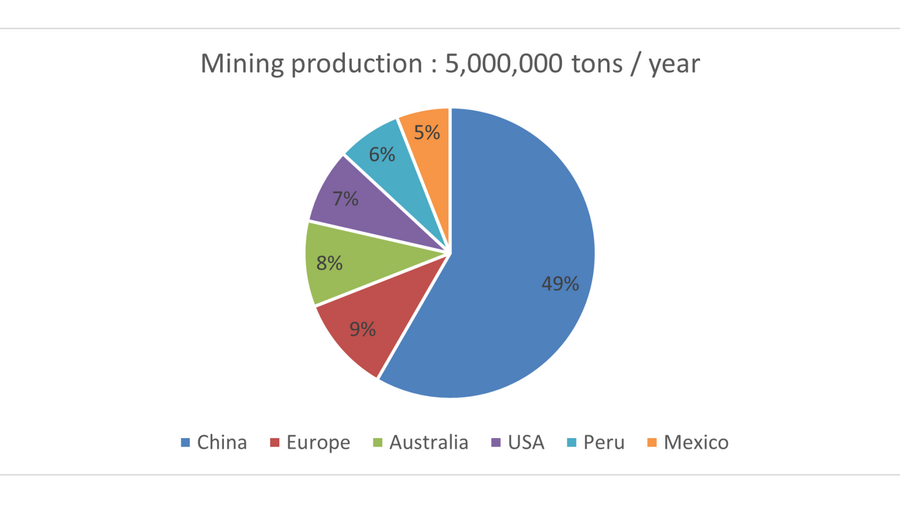
Global consumption is around 12,500,000 tons per year (100,000 tons for France), of which 7,500,000 tons come from recycling !
Applications
- As shot for hunting, fishing, or adjustable ballast.
- As plates for roofing, radiation protection, or sound insulation.
- As pipes : formerly for water pipes.
- In industrial and technical products: balancing weights, sealing weights, bowling pins, etc.
- Alloyed with other metals for telecommunications, cables, connections, chemical industry, etc.
Characteristics of pure lead
- Density: 11.35.
- Melting point: 327°C. Low melting point = reduced energy costs compared to other metals.
- Very malleable, but not very strong when pure.
Health and safety
Lead is toxic if ingested or inhaled in high doses, and can cause lead poisoning. Children are particularly susceptible. Regulations set strict thresholds and require medical monitoring, hygiene procedures, and specific treatment of contaminated water and waste in industrial settings. In its metallic form, lead is stable and not very soluble ; it is mainly its oxides and vapors that pose a risk.
"This image reflects an exploration of sound and visual forms and volumes, revealing the mineral form of lead, galena. On the planet Venus, this crystallized metal is found falling on the peaks of certain Venusian volcanoes, such as Maat Mons."
Visuals : Still Snowing on venus, Sophie Keraudren - Hartenberger.

